Peter Wolters AC microLine® Double Sided Lapping Machines
The high productivity double sided lapping machines of the Peter Wolters AC microLine® range display state-of-the-art design and concept. The modular system of main components together with the precision of the latest control-, drive and measuring technologies superb process reliability and make the system simple to operate. Easily removable machine linings and fully covered process areas give the best accessibility and industrial safety. For automatic loading and unloading, the upper wheel can be swung out.
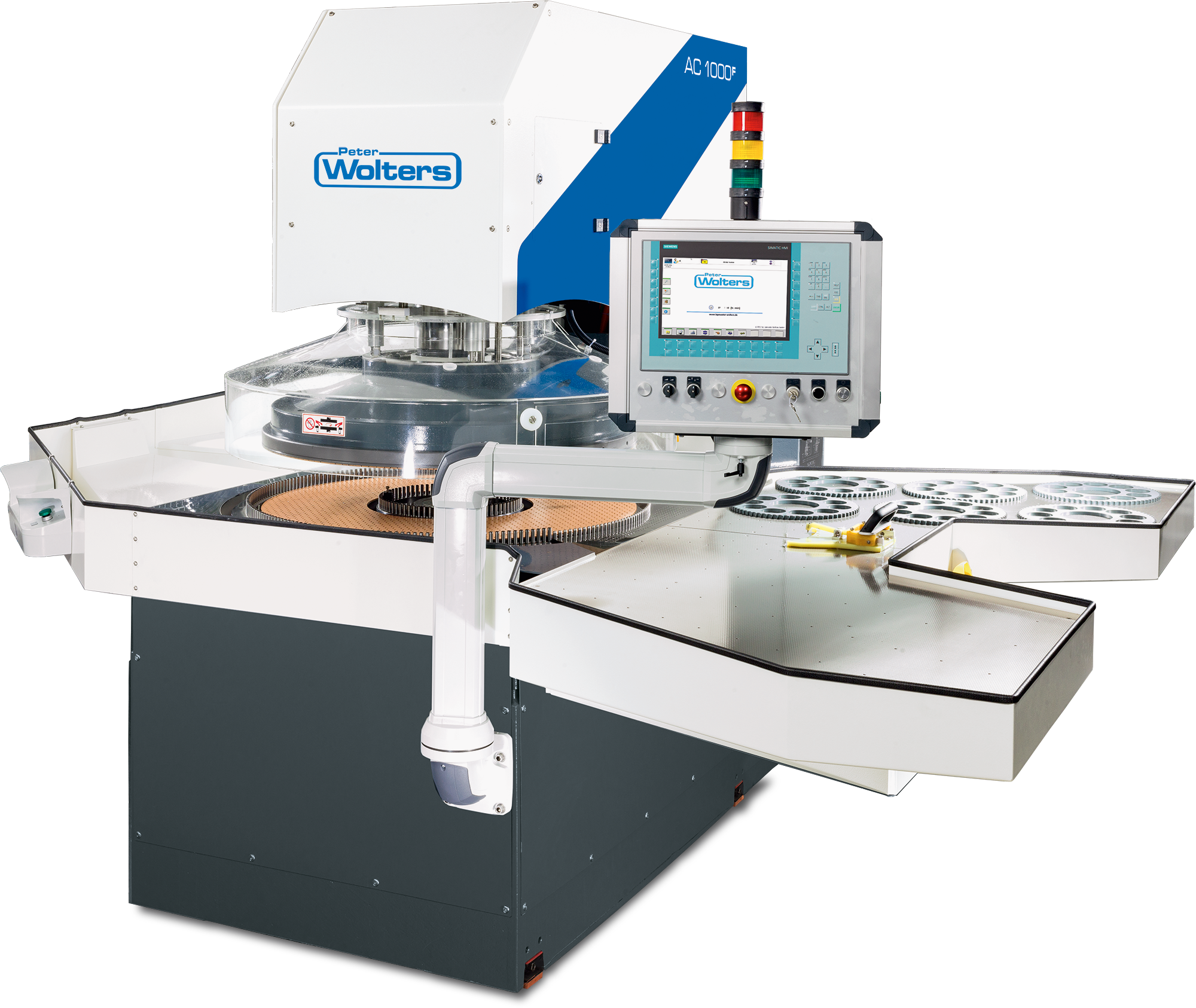

Durability, reliability, low cost of ownership, variety in applications and automation solutions - these are the outstanding features which characterize every Peter Wolters AC microLine® machine. For further increase of productivity, all machines can be equipped with automation setups. Choose between semi and fully automated versions. These automation choices guarantee optimal unit cost combined with high throughput and, therefore, the most economic solution.
Fundamental Lapping Theory
The basic theory of lapping starts with the components being placed within the confines of conditioning rings directly onto the surface of a rotating lap plate that is coated with a precision film layer of slurry. The components should never come into direct contact with the lap plate surface. Through powered lap plate rotation, the loose and rolling abrasive particles within the slurry layer transfer cutting energy with their sharp cutting edges by penetrating the contact surface of the components removing microscopic chips of material. Concurrently the abrasive is acting on the lap plate via the contact surface of both the components and conditioning rings causing wear that when controlled by adjustable radial ring position will effect spherical curvature changes to maintain a flat lap plate condition.
Lapping successfully: Factors to consider
- Type of material being processed
- Speed of plate
- Pressure on work-piece
- Plate material
- Size and type of abrasive
- Vehicle used
- Flatness of plate
- Feed system
- Method of charging and conditioning the plate
- Plate temperature.